تست سمیت ژنی | Ames Test
در مجموعه آزمایشگاه های همکار کیاژن فارما، جهت انجام تست سمیت ژنی Ames ، از کشت تازه سویه های باکتری سالمونلا تیفی موریوم در فاز late exponential یا early stationary به روش plate incorporation method without metabolic activation استفاده می شود.
بدین منظور سوسپانسیون باکتری در معرض ماده آزمایشی و بر روی پلیت حاوی حداقل مواد مغزی قرار خواهد گرفت. بعد از دوره انکوباسیون، تعداد کلونی های ایجاد شده در هر پلیت شمرده و با گروه کنترل مقایسه خواهد شد. تشکیل کلنی حاکی از ایجاد موتاسیون در ژن است.
#تست ایمز#آزمون ایمز#ames assay#ames tests#salmonella typhimurium#سالمونلا تیفی موریوم#تست سمیت ژنی#jsj sldj Ckd#Hcl,k sldj Ckd hdlc#hdlc jsj#Hcl,k hdlc#jsj hdlc
روش کار
- شرایط کشت شامل سویه های باکتری، ماده آزمایشی و یک فعال کننده متابولیک (S9 mix) مخلوط شده در آگار است که روی Minimal Agar Plate ریخته شده است.
- محیط کشت به مدت ۴۸ ساعت در انکوباتور قرار خواهد گرفت و سپس کلنی ها در گروه های تیمار و شاهد، شمارش و با هم مقایسه خواهند شد.
- جهت انجام آزمون از 2 گروه شاهد مثبت S9 (حاوی ماده 2-Anthramine) و فاقد S9 (حاوی ماده های Sodium Azide, 2-Nitrofluorine, Mitomycin C) می باشد.
#تست ایمز#آزمون ایمز#ames assay#ames tests#salmonella typhimurium#سالمونلا تیفی موریوم#تست سمیت ژنی#jsj sldj Ckd#Hcl,k sldj Ckd hdlc#hdlc jsj#Hcl,k hdlc#jsj hdlc
آنالیز آماری داده ها
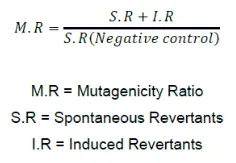
از روش ‘two-fold rule’ جهت آنالیز آماری داده ها استفاده خواهد شد، بدین منظور میزان جهش (mutagenicity ratio) بر اساس تعداد کلنی های شمارش شده بر روی پلیت اندازه گیری شده و با استفاده از فرمول زیر داده ها نتیجه گیری خواهد شد.
#تست ایمز#آزمون ایمز#ames assay#ames tests#salmonella typhimurium#سالمونلا تیفی موریوم#تست سمیت ژنی#jsj sldj Ckd#Hcl,k sldj Ckd hdlc#hdlc jsj#Hcl,k hdlc#jsj hdlc
حالت بک گراند lawn در گروه تیمار نیز، نشان دهنده bacterial toxicity است.
#تست ایمز#آزمون ایمز#ames assay#ames tests#salmonella typhimurium#سالمونلا تیفی موریوم#تست سمیت ژنی#jsj sldj Ckd#Hcl,k sldj Ckd hdlc#hdlc jsj#Hcl,k hdlc#jsj hdlc
تایید ژنوتایپ سویه های باکتری | Genotype Assessment
در بخش میکروبی کیاژن فارما، زمانیکه تعداد موارد spontaneous revertants در کشت باکتری افزایش یابد، آزمون های ژنونیپ سویه های سالمونلا انجام خواهد شد که شامل بررسی سویه های باکتری از نظر نیاز به هیستیدین، rfa mutation، uvrB mutation و R-factor می باشد.
#سمیت ژنی ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی ایمز#سمیت ژنی به روش ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی به روش ایمز
سویه های وابسته به هیستیدین | Histidine Requirement
در بخش میکروبی کیاژن فارما، جهت بررسی ویژگی His– سویه های باکتری از محیط Histidine/Biotin استفاده خواهد شد.
#سمیت ژنی ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی ایمز#سمیت ژنی به روش ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی به روش ایمز
سویه های دارای ویژگی rfa mutation
در بخش میکروبی کیاژن فارما، جهت بررسی deep rough (rfa) سویه های باکتری از روش Crystal Violet Sensitivity استفاده خواهد شد.
#سمیت ژنی ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی ایمز#سمیت ژنی به روش ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی به روش ایمز
سویه های حساس به نور فرابنفش | uvrB mutation
در بخش میکروبی کیاژن فارما، جهت بررسی موتاسیون uvrB از تابش نور فرابنفش استفاده خواهد شد.
#سمیت ژنی ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی ایمز#سمیت ژنی به روش ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی به روش ایمز
سویه های حاوی پلاسمید |R-factor
در بخش میکروبی کیاژن فارما، جهت بررسی حضور پلاسمید R-factor از روش Ampicillin/Tetracycline Plates استفاده خواهد شد.
#سمیت ژنی ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی ایمز#سمیت ژنی به روش ایمز#سمیت ژنتیکی به روش ایمز
استاندارد های زیست سازگاری | References
ISO 10993-1: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Evaluation and testing within a risk management process.
ISO 10993-2: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Animal welfare requirements.
ISO 10993-3: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Tests for genotoxicity, carcinogenicity and reproductive toxicity.
ISO 10993-4: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Selection of tests for interactions with blood.
ISO 10993-5: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Tests for in vitro cytotoxicity.
ISO 10993-6: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Tests for local effects after implantation.
ISO 10993-7: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Ethylene oxide sterilization residuals.
ISO 10993-8: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Selection and qualification of reference materials for biological tests.
ISO 10993-9: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Framework for identification and quantification of potential degradation products.
ISO 10993-10: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Tests for skin sensitization.
ISO 10993-11: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Tests for systemic toxicity.
ISO 10993-12: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Sample preparation and reference materials.
ISO 10993-13: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Identification and quantification of degradation products from polymeric medical devices.
ISO 10993-14: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Identification and quantification of degradation products from ceramics.
ISO 10993-15: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Identification and quantification of degradation products from metals and alloys.
ISO 10993-16: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Toxicokinetic study design for degradation products and leachables.
ISO 10993-17: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Toxicological risk assessment of medical device constituents.
ISO 10993-18: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Chemical characterization of medical device materials within a risk management process.
ISO 10993-19: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Physico-chemical, morphological and topographical characterization of materials.
ISO 10993-20: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Principles and methods for immunotoxicology testing of medical devices.
ISO 10993-22: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Guidance on nanomaterials.
ISO 10993-23: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices – Tests for irritation.
OECD Test No. 401: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Oral Toxicity.
OECD Test No. 402: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Dermal Toxicity.
OECD Test No. 403: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Inhalation Toxicity.
OECD Test No. 404: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Dermal Irritation/Corrosion.
OECD Test No. 405: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Eye Irritation/Corrosion.
OECD Test No. 406: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Skin Sensitisation.
OECD Test No. 407: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Repeated Dose 28-day Oral Toxicity Study in Rodents.
OECD Test No. 408: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Repeated Dose 90-Day Oral Toxicity Study in Rodents.
OECD Test No. 409: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Repeated Dose 90-Day Oral Toxicity Study in Non-Rodents.
OECD Test No. 410: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Repeated Dose Dermal Toxicity: 21/28-day Study.
OECD Test No. 411: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Subchronic Dermal Toxicity: 90-day Study.
OECD Test No. 412: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Subacute Inhalation Toxicity: 28-Day Study.
OECD Test No. 413: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Subchronic Inhalation Toxicity: 90-day Study.
OECD Test No. 414: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Prenatal Developmental Toxicity Study.
OECD Test No. 415: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – One-Generation Reproduction Toxicity Study.
OECD Test No. 416: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Two-Generation Reproduction Toxicity.
OECD Test No. 417: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Toxicokinetics.
OECD Test No. 418: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Delayed Neurotoxicity of Organophosphorus Substances Following Acute Exposure.
OECD Test No. 419: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Delayed Neurotoxicity of Organophosphorus Substances: 28-day Repeated Dose Study.
OECD Test No. 420: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Oral Toxicity – Fixed Dose Procedure.
OECD Test No. 421: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Reproduction/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test.
OECD Test No. 422: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Combined Repeated Dose Toxicity Study with the Reproduction/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test.
OECD Test No. 423: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Oral toxicity – Acute Toxic Class Method.
OECD Test No. 424: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Neurotoxicity Study in Rodents.
OECD Test No. 425: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Oral Toxicity: Up-and-Down Procedure.
OECD Test No. 426: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Developmental Neurotoxicity Study.
OECD Test No. 427: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Skin Absorption: In Vivo Method.
OECD Test No. 428: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Skin Absorption: In Vitro Method.
OECD Test No. 429: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Skin Sensitisation.
OECD Test No. 430: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vitro Skin Corrosion: Transcutaneous Electrical Resistance Test Method (TER).
OECD Test No. 431: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In vitro skin corrosion: reconstructed human epidermis (RHE) test method.
OECD Test No. 432: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vitro 3T3 NRU Phototoxicity Test.
OECD Test No. 433: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Inhalation Toxicity: Fixed Concentration Procedure.
OECD Test No. 434: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Dermal Toxicity – Fixed Dose Procedure.
OECD Test No. 435: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vitro Membrane Barrier Test Method for Skin Corrosion.
OECD Test No. 436: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Acute Inhalation Toxicity – Acute Toxic Class Method.
OECD Test No. 437: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Bovine Corneal Opacity and Permeability Test Method for Identifying i) Chemicals Inducing Serious Eye Damage and ii) Chemicals Not Requiring Classification for Eye Irritation or Serious Eye Damage.
OECD Test No. 438: Isolated Chicken Eye Test Method for Identifying i) Chemicals Inducing Serious Eye Damage and ii) Chemicals Not Requiring Classification for Eye Irritation or Serious Eye Damage.
OECD Test No. 439: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vitro Skin Irritation: Reconstructed Human Epidermis Test Method.
OECD Test No. 440: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Uterotrophic Bioassay in Rodents.
OECD Test No. 441: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Hershberger Bioassay in Rats.
OECD Test No. 442A: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Skin Sensitization – Local Lymph Node Assay: DA.
OECD Test No. 442B: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Skin Sensitization – Local Lymph Node Assay: BrdU-ELISA or –FCM.
OECD Test No. 442C: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Chemico Skin Sensitisation – Assays addressing the Adverse Outcome Pathway key event on covalent binding to proteins.
OECD Test No. 442D: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vitro Skin Sensitisation – ARE-Nrf2 Luciferase Test Method.
OECD Test No. 442E: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – 442E: In Vitro Skin Sensitisation – In Vitro Skin Sensitisation assays addressing the Key Event on activation of dendritic cells on the Adverse Outcome Pathway for Skin Sensitisation.
OECD Test No. 443: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Extended One-Generation Reproductive Toxicity Study.
OECD Test No. 451: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Carcinogenicity Studies.
OECD Test No. 452: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Chronic Toxicity Studies.
OECD Test No. 453: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Combined Chronic Toxicity/Carcinogenicity Studies.
OECD Test No. 455: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Performance-Based Test Guideline for Stably Transfected Transactivation In Vitro Assays to Detect Estrogen Receptor Agonists and Antagonists.
OECD Test No. 456: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – H295R Steroidogenesis Assay.
OECD Test No. 457: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – BG1Luc Estrogen Receptor Transactivation Test Method for Identifying Estrogen Receptor Agonists and Antagonists.
OECD Test No. 458: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Stably Transfected Human Androgen Receptor Transcriptional Activation Assay for Detection of Androgenic Agonist and Antagonist Activity of Chemicals.
OECD Test No. 460: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Fluorescein Leakage Test Method for Identifying Ocular Corrosives and Severe Irritants.
OECD Test No. 471: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Bacterial Reverse Mutation Test.
OECD Test No. 473: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vitro Mammalian Chromosomal Aberration Test.
OECD Test No. 474: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Mammalian Erythrocyte Micronucleus Test.
OECD Test No. 475: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Mammalian Bone Marrow Chromosomal Aberration Test.
OECD Test No. 476: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Tests using the Hprt and xprt genes.
OECD Test No. 477: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Genetic Toxicology: Sex-Linked Recessive Lethal Test in Drosophila melanogaster.
OECD Test No. 478: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Rodent Dominant Lethal Test.
OECD Test No. 479: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Genetic Toxicology: In vitro Sister Chromatid Exchange Assay in Mammalian Cells.
OECD Test No. 480: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Genetic Toxicology: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Gene Mutation Assay.
OECD Test No. 481: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Genetic Toxicology: Saacharomyces cerevisiae, Miotic Recombination Assay.
OECD Test No. 482: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Genetic Toxicology: DNA Damage and Repair, Unscheduled DNA Synthesis in Mammalian Cells in vitro.
OECD Test No. 483: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Mammalian Spermatogonial Chromosomal Aberration Test.
OECD Test No. 484: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Genetic Toxicology: Mouse Spot Test.
OECD Test No. 485: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Genetic toxicology, Mouse Heritable Translocation Assay.
OECD Test No. 486: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Unscheduled DNA Synthesis (UDS) Test with Mammalian Liver Cells in vivo.
OECD Test No. 487: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test.
OECD Test No. 488: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Transgenic Rodent Somatic and Germ Cell Gene Mutation Assays.
OECD Test No. 489: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vivo Mammalian Alkaline Comet Assay.
OECD Test No. 490: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In Vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Tests Using the Thymidine Kinase Gene.
OECD Test No. 491: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Short Time Exposure In Vitro Test Method for Identifying i) Chemicals Inducing Serious Eye Damage and ii) Chemicals Not Requiring Classification for Eye Irritation or Serious Eye Damage.
OECD Test No. 492: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Reconstructed human Cornea-like Epithelium (RhCE) test method for identifying chemicals not requiring classification and labelling for eye irritation or serious eye damage.
OECD Test No. 493: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Performance-Based Test Guideline for Human Recombinant Estrogen Receptor (hrER) In Vitro Assays to Detect Chemicals with ER Binding Affinity.
OECD Test No. 494: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Vitrigel-Eye Irritancy Test Method for Identifying Chemicals Not Requiring Classification and Labelling for Eye Irritation or Serious Eye Damage.
OECD Test No. 495: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Ros (Reactive Oxygen Species) Assay for Photoreactivity.
OECD Test No. 496: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In vitro Macromolecular Test Method for Identifying Chemicals Inducing Serious Eye Damage and Chemicals Not Requiring Classification for Eye Irritation or Serious Eye Damage.
OECD Test No. 497: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – Defined Approaches on Skin Sensitisation.
OECD Test No. 498: Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals – In vitro Phototoxicity – Reconstructed Human Epidermis Phototoxicity test method.
OECD Test No. 19: Guidance Document on the Recognition, Assessment and Use of Clinical Signs as Humane Endpoints for Experimental Animals Used in Safety Evaluation. Environmental Health and Safety Monograph Series on Testing and Assessment.
#تست ایمز#آزمون ایمز#ames assay#ames tests#salmonella typhimurium#سالمونلا تیفی موریوم#تست سمیت ژنی#jsj sldj Ckd#Hcl,k sldj Ckd hdlc#hdlc jsj#Hcl,k hdlc#jsj hdlc










دیدگاهها
هیچ دیدگاهی برای این خدمت نوشته نشده است.